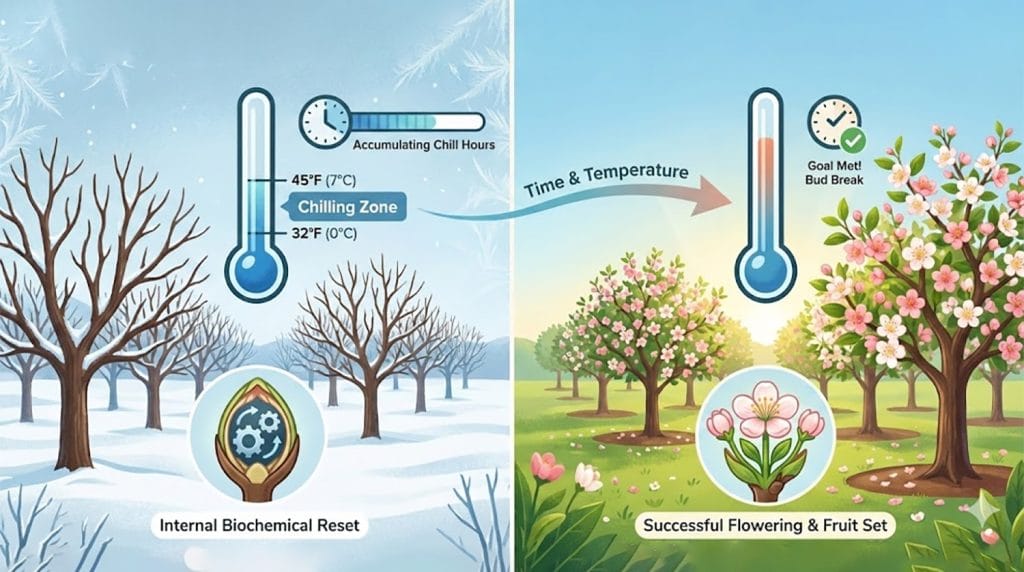
Apple growing in Kashmir has always depended on one quiet but powerful factor: winter cold. Long before buds swell and blossoms appear, apple trees need enough exposure to cold temperatures to wake up properly in spring. This winter cold is measured as chilling hours—and understanding it is becoming more important than ever for Kashmir’s orchards.
This simple guide explains what chilling hours are, why they matter, how they are calculated, and how Orchardly turns this science into practical insights for apple growers.
What are Chilling Hours
Imagine sending your apple trees on a mandatory cold vacation. That’s essentially what chilling hours provide. It’s defined as the cumulative period during which apple trees are exposed to cold temperatures, generally between 32°F to 45°F (0°C to 7°C), during their winter dormancy.
Chilling hours are essential for breaking endodormancy, that deep slumber trees enter to survive winter. This cold exposure fuels proper flower bud development, priming the tree for a vibrant spring bloom. Moreover, it acts as a hormonal reset button, breaking down growth-suppressing hormones like Abscisic Acid (ABA) while simultaneously boosting growth hormones like Gibberellins (GA).
Why Chilling Hours Matter
Apple trees go into winter dormancy to protect themselves from cold damage. During this rest period, buds will not grow—even if conditions look favorable—until they have received enough cold exposure.
If chilling requirements are not met, growers may see:
- Delayed or uneven bud break
- Poor flowering
- Reduced fruit set
- Irregular fruit size and lower yields
Traditionally, Kashmir’s cold winters naturally fulfilled this need. But warming winters and fluctuating temperatures are making chill accumulation less predictable, especially in lower elevations.
Chilling Requirements of various Apple Varieties
Different apple varieties need different amounts of winter chill. Some need long, cold winters, while others can manage with less.
Approximate chilling requirements for common Kashmir varieties:
| Apple Variety | Typical Chill Requirement |
|---|---|
| Delicious group (Royal, Red, Starking) | 1,000–1,200 hours |
| Red Delicious | 1,000–1,100 hours |
| Golden Delicious | 800–1,000 hours |
| Gala | 600–800 hours |
| Fuji | 900–1,100 hours |
When chill requirements are met:
- Bud break is uniform
- Flowering is synchronized
- Fruit set and quality improve
The Science Behind Chilling Hours
Inside each apple bud are growth-inhibiting compounds that keep it dormant. Cold temperatures slowly break down these inhibitors.
- Cool temperatures → reduce dormancy blockers
- Excessive warmth → can slow or even reverse progress
This is why not all cold hours are equally effective, and why modern chill models exist.
How Are Chilling Hours Calculated?
Over time, scientists have developed different models to measure chill more accurately.
1️⃣ Simple Chilling Hours Model
- Counts every hour between a fixed temperature range (often 0–7°C)
- Easy to understand
- Less accurate during warm winters
2️⃣ Utah Model
- Assigns weights to different temperatures
- Some temperatures add chill, some add less, and warm temperatures can subtract chill
- Useful, but sensitive to sudden warm spells
3️⃣ Positive Utah Model
- A safer version of Utah
- Does not subtract chill during warm periods
- Better suited for regions with fluctuating winters
4️⃣ Dynamic Model (Chill Portions)
- Most advanced and climate-resilient
- Chill accumulates in stable portions rather than simple hours
- Performs best in temperate and warming climates like Kashmir
Other regional and modified models exist, but globally the Dynamic Model is increasingly preferred for apples.
How Orchardly Uses Chilling Hours
Orchardly goes beyond simple counting. By crunching hourly temperature data from diverse sources, including weather stations and smart sensors, and applying sophisticated algorithms, Orchardly delivers predictive power. Inside Orchardly, chilling hours are:
- Calculated from local weather data
- Processed using multiple chill models (including Dynamic and Utah variants)
- Combined with heat accumulation and phenology data
This allows Orchardly to:
- Track real-time chill accumulation
- Estimate whether your orchard has met varietal requirements
- Support bud break, flowering, and yield prediction algorithms
- Detect early warning signs of chill deficiency stress
From Winter Chill to Smart Decisions
Orchardly’s AI isn’t merely counting hours; it’s learning and adapting, providing personalized insights to secure your future harvests. Chilling hours for us are not just a number—they are a signal.
Orchardly integrates chilling data with:
- Variety-specific requirements
- Orchard location and elevation
- Historical climate trends
This transforms raw weather data into actionable insights, helping growers:
- Understand seasonal risks early
- Plan orchard operations better
- Adapt to changing winter patterns
Orchardly offers actionable recommendations, from selecting the right varieties for your evolving climate to timing interventions like applying dormancy-breaking agents or initiating thinning. Orchardly provides tailored advice to optimize your specific orchard’s needs.
Orchardly: Your Intelligent Companion
As winters change, relying only on experience is no longer enough. Data-backed decisions are becoming essential for sustainable apple production in Kashmir. With Orchardly :
- You don’t just see the weather—you understand its impact
- You don’t just track cold—you know what it means for your trees
- You don’t react late—you prepare early
Orchardly helps your apples stay one step ahead.