The pH of soil is an important factor that controls several soil activities. Soil pH, often referred to as the “master variable,” is crucial for plant growth and biomass yield. It regulates chemical and biochemical processes, affecting nutrient availability. Maintaining the right pH is essential for crop growth, nutrient uptake, and agricultural yields. Understanding and controlling soil pH is crucial for farmers to provide the best circumstances for their chosen crops since different plants thrive in different pH ranges
What is pH?
Soil pH in common language can be defined as the measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil. pH value is actually a measure of hydrogen ion concentration. The pH range for soil solution varies from 0-14. Soils with a pH below 7 are considered acidic, while those above 7 are alkaline.
The role of nutrients in plant growth
Nutrients are essential for plant growth and development, including macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, and micronutrients like iron and zinc. Nitrogen is crucial for leafy growth, phosphorus aids in root development and flowering, and potassium regulates physiological processes. Micronutrients like iron and zinc are vital for enzyme activity and overall plant health. Adequate nutrient availability ensures plants can synthesize essential compounds, perform photosynthesis, and respond to environmental stresses.
pH and Nutrient Availability
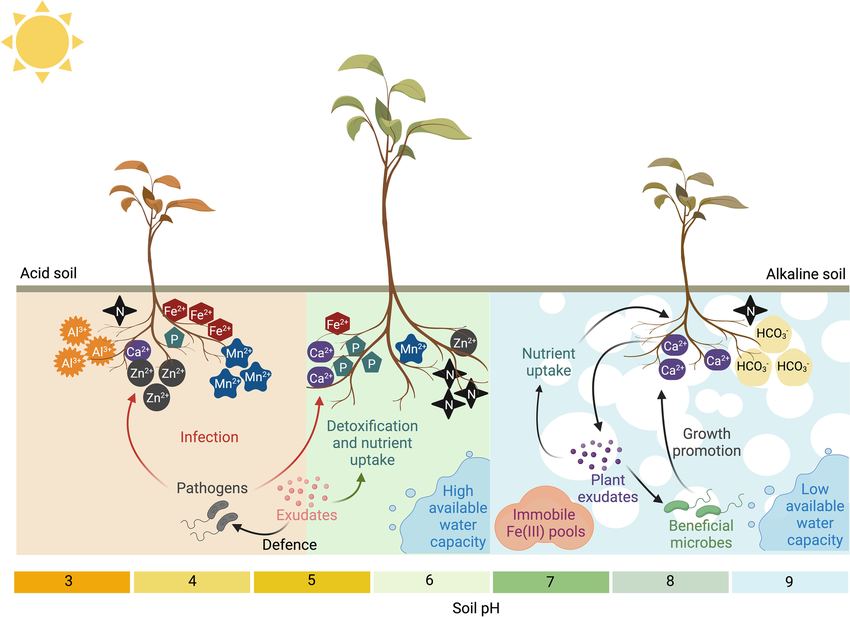
Soil pH significantly impacts nutrient uptake and plant health. Acidic soils restrict access to calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus, while alkaline soils limit iron, manganese, and zinc availability. Acidic soils may lead to aluminum and manganese toxicity, and alkaline soils reduce phosphorus accessibility. Maintaining a pH of 6-7 (slightly acidic to neutral) ensures optimal nutrient access, supporting healthy plant growth. pH management through soil testing and adjustments is essential to facilitate efficient nutrient absorption, promoting healthy plant growth.
In the world of apple orchards, the relevance of soil pH to nutrient availability cannot be overstated. The soil’s pH significantly impacts nutrient uptake by apple trees, directly affecting their health and productivity.
Optimal pH ranges for different nutrients
Essential plant nutrients have specific pH preferences for optimal availability: nitrogen (pH 6.0-7.0), phosphorus (pH 6.0-7.5), and potassium (pH-insensitive within typical ranges). Micronutrients like iron (pH 5.5-6.5), manganese, and zinc (pH 5.5-7.0) also have distinct preferences. Understanding these pH ranges is essential for effective nutrient management and healthy plant growth. Recognizing these pH ranges is crucial for effective nutrient management and fostering healthy plant growth.
Importance of soil pH testing
Soil pH testing is crucial in agriculture for several reasons. It provides insights into soil health and fertility, allowing growers to determine nutrient availability. Soil pH can fluctuate over time due to weather conditions and farming practices, making regular testing essential for proactive pH management. It also influences microbial activity and beneficial soil organism health, affecting soil’s capacity to break down organic matter and release nutrients.
Want to get your soil tested? Book a soil test from Orchardly and get personalized recommendations from our experts.
Methods to adjust soil pH
- Liming for Acidity: Add limestone or dolomite to raise pH in acidic soils.
- Acidification for Alkalinity: Lower pH in alkaline soils by incorporating sulfur, gypsum, or ammonium-based fertilizers.
- Organic Matter: Incorporate organic matter to buffer pH and reduce rapid fluctuations.
Soil pH adjustment is gradual; conduct soil tests to determine the right amendments. Choose the method and material based on initial pH, plant requirements, and long-term soil management goals.
Tips for farmers
Regular soil pH testing is vital for soil health and productivity as it affects nutrient availability and microbial activity. Most plants thrive in pH 6.0 to 7.0 (slightly acidic to neutral) conditions. Monitoring and adjusting soil pH support healthier plant growth, boosting nutrient uptake for higher crop yields. Choosing plants suited to your soil pH is crucial for success, as different plants have specific pH preferences.
Book a soil test from Orchardly and get personalized recommendations from our experts.
In Kashmir region, where apple cultivation is a way of life, the importance of soil pH management cannot be overstated. It is a key aspect of responsible and sustainable farming practices. Regular soil pH testing is vital for ensuring the health and productivity of apple orchards in Kashmir. As most apple tree varieties thrive in slightly acidic to neutral conditions (pH 6.0 to 7.0), monitoring and adjusting soil pH is essential.
Responsible pH management benefits agriculture and the environment, emphasizing our shared responsibility for a greener future.


